JSON
(Note: this article is copied from http:\\json.org)
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format. It is easy for humans to read and write. It is easy for machines to parse and generate. It is based on a subset of the JavaScript Programming Language, Standard ECMA-262 3rd Edition - December 1999. JSON is a text format that is completely language independent but uses conventions that are familiar to programmers of the C-family of languages, including C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Perl, Python, and many others. These properties make JSON an ideal data-interchange language.
JSON is built on two structures:
- A collection of name/value pairs. In various languages, this is realized as an object, record, struct, dictionary, hash table, keyed list, or associative array.
- An ordered list of values. In most languages, this is realized as an array, vector, list, or sequence.
These are universal data structures. Virtually all modern programming languages support them in one form or another. It makes sense that a data format that is interchangeable with programming languages also be based on these structures.
In JSON, they take on these forms:
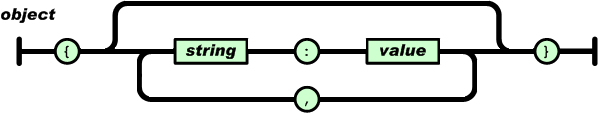
An object is an unordered set of name/value pairs. An object begins with { (left brace) and ends with } (right brace). Each name is followed by : (colon) and the name/value pairs are separated by , (comma).
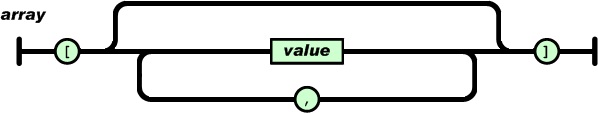
An array is an ordered collection of values. An array begins with [ (left bracket) and ends with ] (right bracket). Values are separated by , (comma).
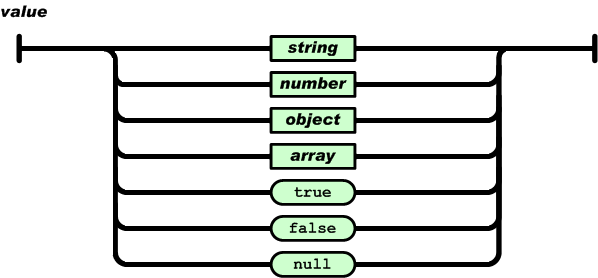
A value can be a string in double quotes, or a number, or true or false or null, or an object or an array. These structures can be nested.
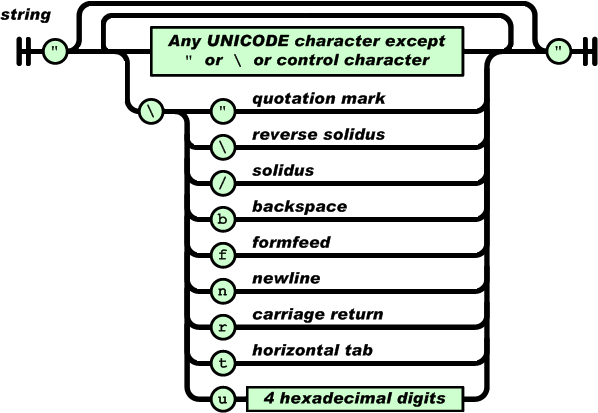
A string is a sequence of zero or more Unicode characters, wrapped in double quotes, using backslash escapes. A character is represented as a single character string. A string is very much like a C or Java string.
A number is very much like a C or Java number, except that the octal and hexadecimal formats are not used.
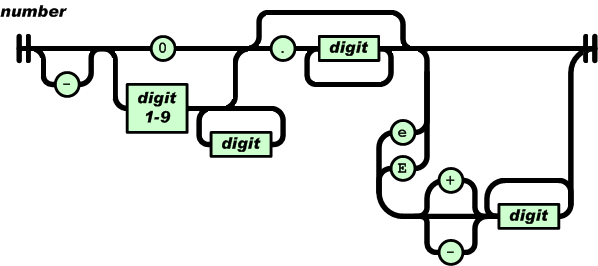
Whitespace can be inserted between any pair of tokens. Excepting a few encoding details, that completely describes the language.
